The Hidden Powers that Govern the Internet
Have you ever stopped to wonder who controls the internet? In this blog post, we’ll explore the various organizations and bodies that play a role in governing the internet, and how they work together to ensure its stability, security, and interoperability.
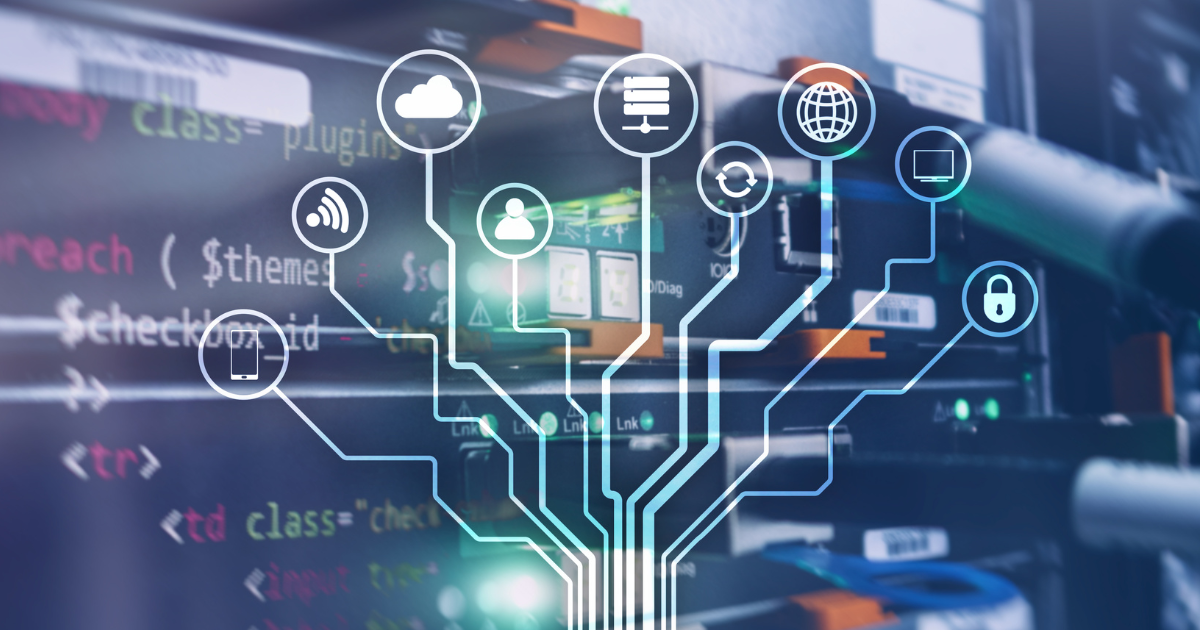
The internet is a decentralized network of interconnected computer networks and devices. It is not owned or controlled by any one entity, but is rather governed by a number of different organizations and standards bodies. One of the most important of these organizations is the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). ICANN is responsible for coordinating the global internet’s systems of unique identifiers, including domain names, IP addresses, and protocol parameters. ICANN ensures that each device connected to the internet has a unique address and that the internet’s naming and addressing systems work properly.
ICANN operates under a set of agreements with the U.S. Department of Commerce, which were designed to gradually transition the organization to a more global and multistakeholder model. In 2016, the transition was completed, and ICANN became a fully independent organization, with a more diverse and representative governance structure.
In addition to ICANN, there are a number of other organizations that play a role in governing the internet. For example, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) develops and maintains technical standards for the web, including HTML, CSS, and other web technologies. The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is responsible for developing and maintaining the technical standards and protocols that govern the operation of the internet. And the Internet Society (ISOC) is a nonprofit organization that works to promote the open development, evolution, and use of the internet around the world.
All of these organizations work together to ensure that the internet remains stable, secure, and interoperable. They collaborate on the development of technical standards and protocols, and help to resolve issues that may arise on the internet, such as network congestion, cyber attacks, and disputes over domain names and IP addresses.
The internet is not controlled by any one entity, but is rather governed by a decentralized network of organizations and standards bodies. These organizations work together to ensure the stability, security, and interoperability of the internet, and to develop and maintain the technical standards and protocols that make the internet work. While there may be occasional challenges and disputes that arise, the collaborative nature of internet governance has helped to make the internet the global phenomenon that it is today.