How the Domain Name System Works
Have you ever wondered how your computer knows how to connect to a website when you type in a domain name? The answer lies in the Domain Name System, or DNS. In this post, we’ll take a closer look at what DNS is, how it works, and why it’s so important for the internet.
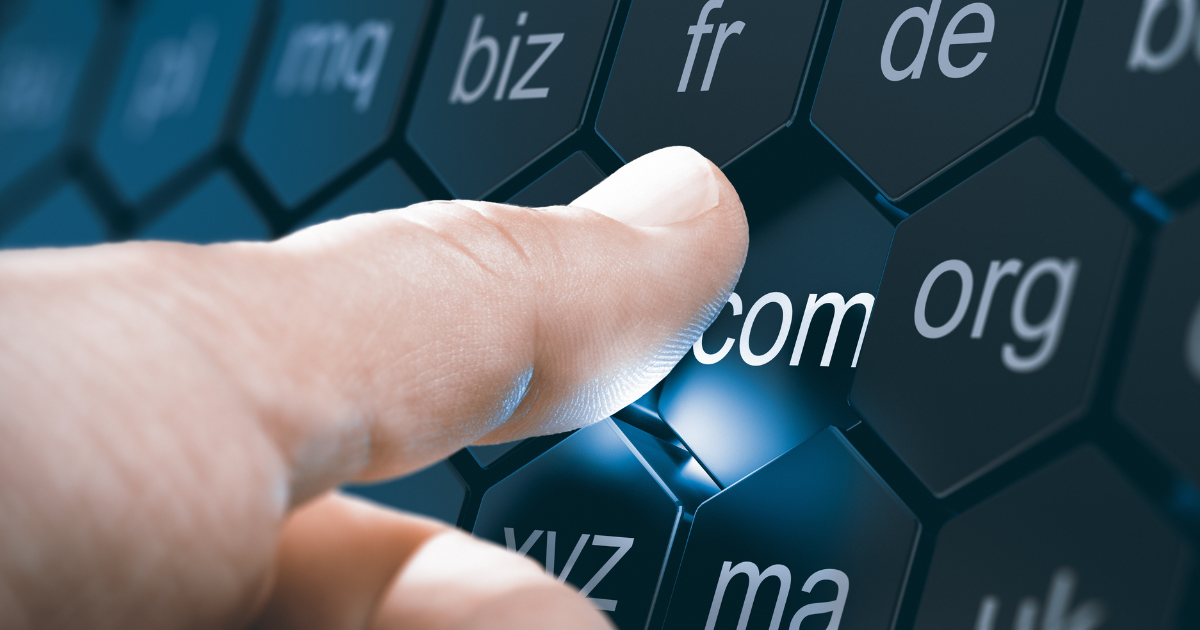
At its core, DNS is a system that maps domain names to IP addresses. When you type a website address into your browser, such as www.example.com, your computer needs to know the IP address of the server that hosts that website in order to connect to it. DNS provides a way to look up the IP address associated with a given domain name.
DNS works by using a distributed database of servers, each of which stores information about a subset of domain names. When you type a domain name into your browser, your computer sends a request to a DNS resolver, which is a server that is responsible for finding the IP address associated with the domain name. The resolver then queries a series of DNS servers, starting with the root server, to find the IP address. Each server in the chain provides more specific information about the domain name until the resolver has the correct IP address.
The DNS system is hierarchical in nature, with the root server at the top, followed by top-level domains (TLDs), such as .com, .org, and .net. Beneath the TLDs are second-level domains (SLDs), such as example.com. Each domain name is unique and can only be registered by one entity at a time.
DNS is critical to the functioning of the internet, as it allows users to connect to websites, send emails, and perform other online activities. However, DNS is also a prime target for cyberattacks, as it is a central point of control that can be exploited to redirect traffic, intercept emails, and more. To combat these threats, DNS security has become a major concern, with various measures such as DNSSEC and DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) being implemented to improve the security and privacy of the system.
In conclusion, DNS is a fundamental system that underpins the functioning of the internet. It provides a way for domain names to be translated into IP addresses, allowing users to access websites and other online resources. While DNS may seem complex, it is an essential component of the digital infrastructure that we rely on every day.